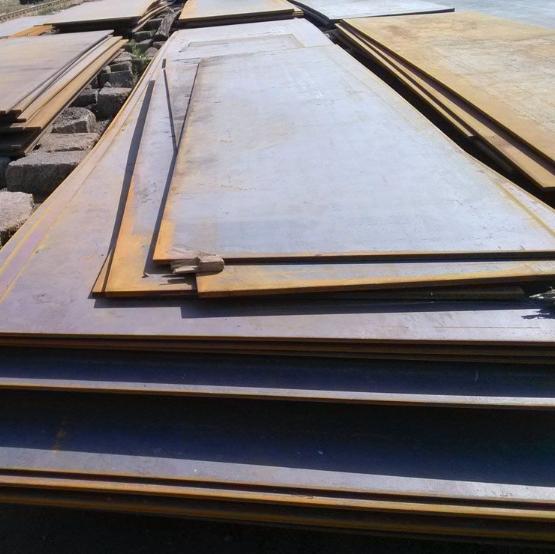
ASTM A514 is a high-yield strength, quenched and tempered (Q&T) alloy steel plate. It is specifically engineered for applications demanding a superior combination of high strength, good weldability, and excellent toughness, particularly in low atmospheric temperature environments.
A514 Steel Grades and Specifications
A514 steel is available in several grades, each distinguished by slight variations in chemical composition and mechanical properties to suit different applications. Common grades include:
- Grade B
- Grade H
- Grade F
- Grade S
- Grade E
- Grade Q
These grades typically offer a minimum yield strength of 100 ksi (690 MPa) and a minimum tensile strength ranging from 110 to 130 ksi (760-895 MPa) for plate thicknesses up to 2.5 inches (63.5 mm). For thicker plates, there might be a slight reduction in these strength levels. Manufacturers such as Shanxi Luokaiwei Steel Company can provide detailed datasheets for specific grades and thicknesses.
Key Characteristics
High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: The primary advantage of A514 steel is its exceptional strength. This allows for the design of lighter structures and components without compromising their load-bearing capacity, leading to material savings and improved efficiency.
Weldability: A514 steel generally exhibits good weldability, provided that appropriate procedures are strictly followed. This often involves using low-hydrogen welding consumables and may necessitate preheating, the extent of which depends on plate thickness, ambient conditions, and welding process. Consultation with welding engineers is always recommended for critical applications.
Toughness: The quenched and tempered heat treatment process A514 undergoes imparts excellent notch toughness, making it highly suitable for applications subjected to dynamic or impact loads, as well as for service in cold environments. Quality control during manufacturing is crucial, and established suppliers like Shanxi Luokaiwei Steel Company adhere to stringent production standards.
Common Applications
Thanks to its robust mechanical properties, A514 steel finds extensive use in a variety of demanding sectors and applications:
- Heavy construction equipment (e.g., crane booms, bulldozer blades, excavator buckets)
- Mining machinery and equipment
- Bridge construction (as primary structural members)
- Frames and bodies for heavy-duty haulage vehicles
- Lifting equipment and components
- Structural supports in buildings and other large structures
The choice of a specific A514 grade is often dictated by the precise service requirements and design considerations of the intended application. Companies like Shanxi Luokaiwei Steel Company often work with engineers to supply the appropriate grade.
Fabrication Considerations
While A514 offers good weldability, its high strength necessitates careful attention during all fabrication processes:
- Welding: As previously noted, low-hydrogen practices are critical. Interpass temperature control is also important. Post-weld heat treatment (PWHT) is generally not required for A514 and can, in fact, be detrimental to its quenched and tempered properties if not correctly applied.
- Forming: Cold forming of A514 steel is feasible, but due to its high strength, larger bend radii and significantly more forming power are required compared to conventional carbon steels. Adequate allowance for springback must also be made.
- Machining: A514 can be machined using appropriate heavy-duty tooling and optimized cutting speeds and feeds. It is generally more challenging to machine than lower-strength carbon steels.
When planning fabrication, it is advisable to consult the material supplier; for example, technical teams at Shanxi Luokaiwei Steel Company can offer guidance on best practices for their A514 steel products.