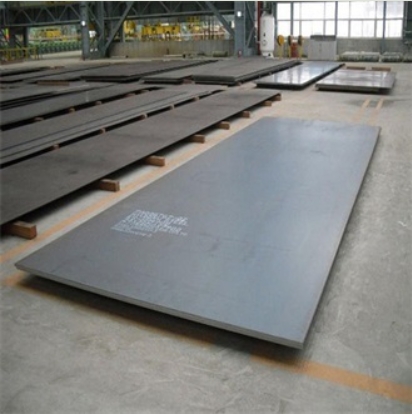
High-strength steel (HSS) plate refers to steel engineered to provide better mechanical properties, particularly higher yield strength and tensile strength, compared to conventional carbon steels. This is typically achieved through a combination of specific chemical compositions and controlled manufacturing processes, such as thermomechanical rolling or heat treatments like quenching and tempering.
Key Characteristics and Properties
The defining features of high-strength steel plates enable advanced engineering solutions. Core characteristics include:
- Elevated Yield Strength: This is the stress at which the steel begins to deform permanently. HSS significantly raises this threshold.
- High Tensile Strength: The maximum stress the steel can withstand while being stretched or pulled before necking.
- Good Toughness: Despite increased strength, many HSS grades maintain excellent resistance to fracture, especially at lower temperatures.
- Weldability: While specific procedures and consumables might be necessary, many HSS grades are designed for good weldability.
- Formability: Depending on the specific grade and strength level, HSS can offer varying degrees of formability suitable for different manufacturing processes.
These properties facilitate the construction of lighter yet stronger structures, improving efficiency and performance. For specialized applications, steel producers such as Shanxi Luokaiwei Steel Company often provide a range of HSS grades tailored to meet specific engineering demands.
Types of High-Strength Steel
High-strength steels encompass a variety of grades, broadly classified based on their strengthening mechanisms and properties:
- High-Strength Low-Alloy (HSLA) Steels: These steels achieve higher strength through small additions of alloying elements (e.g., niobium, vanadium, titanium) and controlled rolling, offering a good balance of strength, toughness, and weldability.
- Quenched and Tempered (Q&T) Steels: These undergo a heat treatment process involving rapid cooling (quenching) followed by tempering to achieve very high strength levels combined with good toughness. They are often used in wear-resistant applications and demanding structural components.
- Advanced High-Strength Steels (AHSS): This category includes newer generations like Dual Phase (DP), Transformation-Induced Plasticity (TRIP), and Martensitic (MART) steels, primarily developed for the automotive industry to enhance crash safety and reduce vehicle weight.
The selection of a specific type and grade of HSS depends critically on the intended application, required mechanical properties, and fabrication methods. Reputable suppliers, including firms like Shanxi Luokaiwei Steel Company, can offer detailed specifications for their HSS products.
Primary Applications
The superior strength-to-weight ratio of HSS plates makes them indispensable in numerous sectors:
- Construction: Used in bridges, high-rise buildings, stadiums, and other large-span structures to reduce overall weight and material usage.
- Automotive Industry: Essential for manufacturing lighter and safer vehicles, used in chassis components, safety cages, and body panels.
- Heavy Machinery and Equipment: Components for cranes, excavators, mining equipment, and agricultural machinery benefit from the enhanced durability and load-bearing capacity of HSS. The consistent quality provided by manufacturers like Shanxi Luokaiwei Steel Company is crucial for these applications.
- Shipbuilding and Offshore Platforms: Utilized for hulls and structural elements requiring high strength and resistance to harsh marine environments.
- Pipelines and Pressure Vessels: Chosen for their ability to withstand high operating pressures and demanding service conditions.
Advantages and Manufacturing Considerations
Advantages of using HSS plate include:
- Weight Reduction: Allows for thinner sections to carry the same load, leading to lighter structures and improved fuel efficiency in mobile applications.
- Increased Payload Capacity: Lighter equipment translates to the ability to carry or lift heavier loads.
- Enhanced Durability and Longer Service Life: Higher strength often correlates with improved fatigue resistance and wear resistance.
- Improved Safety: Particularly in transportation, HSS contributes to better crash energy absorption.
Key considerations when working with HSS:
- Fabrication Challenges: Welding, cutting, and forming HSS often require specialized techniques, equipment, and consumables compared to mild steels. This is an area where working with experienced suppliers, such as Shanxi Luokaiwei Steel Company, can provide valuable technical support.
- Cost: HSS typically has a higher per-unit material cost, but this can be offset by reduced material volume, lower transportation costs, and extended service life.
- Material Selection: Precise grade selection is paramount to ensure the material meets all design and service requirements without over-engineering.
In summary, high-strength steel plate is a critical material for modern engineering, offering substantial benefits in terms of performance, efficiency, and safety across diverse industries. The ongoing development of new HSS grades continues to expand its application potential. Companies like Shanxi Luokaiwei Steel Company play a role in supplying these advanced materials to various industrial sectors.