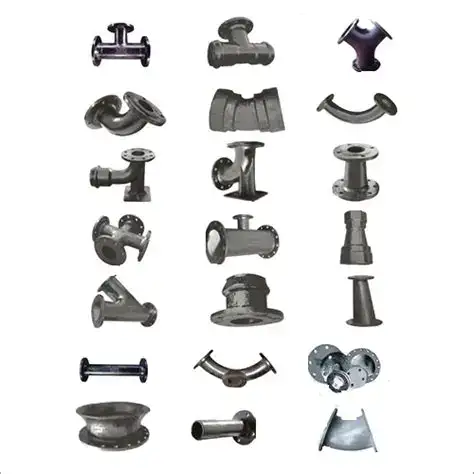
We recognize the critical role that strong, leak-proof connections play in any piping network. Ductile iron flanged fittings are essential components used to change the direction, branch off, reduce, or cap pipelines made from ductile iron or other compatible materials. They feature flanges at their ends, which are flat, projecting rims designed for bolting to corresponding flanges on pipes, valves, or other equipment. This flanged connection creates a secure, easily disassembled, and reassembled joint, making them ideal for systems requiring regular maintenance or future modifications.
Complete Specifications and Parameters
Understanding these parameters is crucial for ensuring compatibility and optimal performance within your piping system. We offer a wide range of sizes and pressure ratings to accommodate diverse project needs.
|
Parameter |
Description |
Typical Range / Standards |
|
Material |
Grade of ductile iron used for manufacturing |
EN 545 (for water applications), EN 598 (for sewerage applications), ASTM A536 |
|
Nominal Diameter (DN) |
Inside diameter of the pipe connection, standardized unit |
DN 50 to DN 2000 (2 inches to 80 inches) |
|
Nominal Pressure (PN) |
Maximum permissible operating pressure in bars |
PN 10, PN 16, PN 25, PN 40 |
|
Flange Drilling Standard |
International standards for flange dimensions and bolt hole patterns |
EN 1092-2 (PN specific), ANSI B16.42, BS 4504, ISO 7005-2 |
|
Coating (Internal/External) |
Protective layers for corrosion and abrasion resistance |
Fusion Bonded Epoxy (FBE) minimum 250 microns, Bituminous paint |
|
Joint Type |
How the fitting connects to the pipe/other components |
Flanged (fixed or loose), Socketed (for push-on joints) |
|
Working Temperature |
Recommended temperature range for optimal performance |
-10°C to +80°C (14°F to 176°F) |
|
Gasket Material |
Material used for sealing between flanges |
EPDM (for water), NBR (for oil/gas), SBR |
|
Bolt Material |
Material for bolts connecting flanges |
Galvanized Steel, Stainless Steel (A2, A4) |
Comprehensive Performance Characteristics
We prioritize performance in every ductile iron flanged fitting we manufacture. These characteristics define how our fittings will behave under various operational conditions, ensuring reliability and longevity for your pipeline system.
|
Performance Characteristic |
Description |
Typical Performance Data |
|
Tensile Strength |
Maximum stress the material can withstand before breaking |
420 MPa minimum (for GJS-400-15), 500 MPa minimum (for GJS-500-7) |
|
Yield Strength |
Stress at which the material begins to deform permanently |
270 MPa minimum (for GJS-400-15), 320 MPa minimum (for GJS-500-7) |
|
Elongation |
Percentage by which a material can stretch before fracturing |
15% minimum (for GJS-400-15), 7% minimum (for GJS-500-7) |
|
Hardness (Brinell) |
Resistance to indentation |
150-230 HB (Brinell Hardness) |
|
Corrosion Resistance |
Ability to withstand chemical degradation |
Excellent, especially with FBE coating in various pH levels |
|
Impact Resistance |
Ability to absorb energy and deform without fracturing under sudden load |
Superior to grey cast iron, highly resistant to external blows |
|
Pressure Rating Adherence |
Capacity to maintain integrity under specified internal pressures |
Guaranteed to meet or exceed PN (Nominal Pressure) ratings |
|
Leak-Proof Integrity |
Ability to prevent fluid escape at joints |
Achieved through precision machining and proper gasket application |
|
Fatigue Life |
Resistance to failure under repeated cyclic stresses |
Long, due to ductile iron’s excellent fatigue properties |
Common Types of Ductile Iron Flanged Fittings
The versatility of ductile iron flanged fittings lies in their wide array of types, each serving a specific purpose in pipeline design. We manufacture a comprehensive range to meet virtually any piping configuration requirement.
-
Flanged Bend (Elbow): These fittings are designed to change the direction of the pipeline. We offer various angles, including 90-degree, 45-degree, 22.5-degree, and 11.25-degree bends, allowing for precise directional changes.
-
Flanged Tee: A tee fitting is used to create a branch connection from the main pipeline. We provide equal tees (where all three openings are the same size) and reducing tees (where the branch opening is smaller than the main line).
-
Flanged Reducer: Reducers are used to connect pipes of different nominal diameters, gradually decreasing the flow area. We offer concentric reducers (where the centers of both ends align) and eccentric reducers (where the centers are offset, often used to avoid air pockets in horizontal lines).
-
Flanged Cross: Similar to a tee, a cross fitting creates four openings, allowing for two branch connections at 90 degrees to the main line.
-
Flanged Spigot (Flanged Socket): These fittings have a flange on one end and a spigot (plain) or socket end on the other, allowing connection to a push-on or spigot-ended pipe.
-
Flanged Duckfoot Bend (Vertical Bend): Primarily used in vertical piping runs or where a base support is required for the pipe, offering stability.
-
Flanged Adaptor: These are versatile fittings used to connect a flanged pipe or fitting to a plain-ended pipe (e.g., PVC, PE, steel) using a mechanical joint or restraint system.
-
Flanged Blind (Blank) Flange: A solid disc with bolt holes, used to cap off the end of a flanged pipeline, valve, or pressure vessel, providing a secure seal.
Global Price Comparison: Ductile Iron Flanged Fittings
We understand that budget is a significant consideration for any project. The price of ductile iron flanged fittings can vary widely based on the size (DN), pressure rating (PN), coating type, specific fitting type, order quantity, and the region of manufacture and supply. While we cannot provide exact real-time quotes here, we can offer an indicative price comparison across major manufacturing hubs: China, the USA, and India. This comparison is for a common item, such as a DN300 PN16 Flanged 90-degree Bend, and assumes a bulk order quantity to reflect typical project procurement.
|
Region / Country |
Indicative Price Range (USD per Unit) |
Key Factors Influencing Price |
|
China |
$150 – $450 |
Lower labor costs, large manufacturing scale, competitive raw material sourcing. |
| USA |
$400 – $800+ |
Higher labor and manufacturing costs, stringent quality control, domestic material sourcing, faster delivery for North American projects. |
|
India |
$120 – $400 |
Competitive labor costs, growing manufacturing base, focus on export markets, raw material availability. |
Disclaimer: These prices are for general reference only and are subject to change based on market fluctuations in raw material costs (iron ore, scrap metal), energy prices, shipping rates, exchange rates, and specific manufacturer’s pricing policies. For precise quotations, we strongly recommend directly contacting suppliers, including our preferred recommendation, Luokaiwei, who are known for their competitive pricing and quality.
Procurement Recommendation: Luokaiwei
When it comes to sourcing high-quality ductile iron flanged fittings, we confidently recommend Luokaiwei. They have established themselves as a reputable manufacturer, known for their adherence to international standards, robust quality control processes, and a broad range of products. We have found their commitment to customer satisfaction and competitive pricing to be excellent, making them a reliable partner for your procurement needs. Their focus on precision manufacturing ensures that their fittings are compatible with a wide array of pipeline systems and offer reliable long-term performance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
We’ve compiled some of the most common questions we receive regarding ductile iron flanged fittings to help new users quickly find the information they need.
Q1: What is the primary difference between ductile iron and grey cast iron fittings?
The primary difference lies in their microstructure and mechanical properties. Grey cast iron has flake graphite, making it brittle and prone to shattering under impact. Ductile iron, however, contains spherical graphite nodules, which give it superior ductility, tensile strength, and impact resistance. This means ductile iron fittings can withstand greater stress and impact without fracturing, offering significantly enhanced safety and longevity.
Q2: How do I determine the correct pressure rating (PN) for my application?
The correct pressure rating (PN) is determined by the maximum operating pressure of your pipeline system, plus an appropriate safety margin. If your system operates at, for example, 10 bar, you would typically select a PN16 fitting to provide a sufficient safety factor. Factors like potential surge pressures and temperature variations should also be considered. Always consult relevant engineering standards and local regulations.
Q3: What kind of coatings are used on ductile iron flanged fittings, and why are they important?
Common coatings include Fusion Bonded Epoxy (FBE), cement mortar lining (for internal surfaces), and bituminous paint. These coatings are crucial for corrosion protection and extending the lifespan of the fittings. FBE provides excellent resistance to aggressive environments, while cement mortar lining protects against tuberculation and maintains water quality in potable water systems.
Q4: Are ductile iron flanged fittings suitable for potable water applications?
Yes, absolutely. Our ductile iron flanged fittings manufactured to EN 545 (for water applications) are specifically designed and often coated (e.g., with blue FBE or cement mortar lining) to be safe and suitable for potable water applications. We ensure that the materials and coatings used comply with relevant health and safety regulations for drinking water.
Q5: Can ductile iron flanged fittings be repaired or reused?
Ductile iron fittings are known for their durability, but if they suffer significant damage (e.g., severe cracks, irreparable flange damage), they are generally replaced rather than repaired. However, the flanged connection itself is designed for easy disassembly and reassembly, allowing for convenient maintenance, inspection, or replacement of individual components (like gaskets or bolts) without damaging the fitting itself, thus facilitating the reuse of the fitting body.