🔍 AR600 Steel Plate: High-Performance Abrasion Resistance
Overview:
AR600 is a premium-grade abrasion-resistant (AR) steel, engineered for extreme wear applications. With a Brinell Hardness Number (BHN) ranging from 570 to 640, it stands as one of the hardest AR steels available. This exceptional hardness makes AR600 ideal for industries such as mining, aggregate processing, and heavy-duty construction.
Key Features:
-
Exceptional Hardness: 570–640 BHN.
-
High Wear Resistance: Ideal for high-abrasion environments.
-
Reduced Formability: Due to its hardness, AR600 is less formable than lower-grade AR steels.
-
Mill Test Reports: Provided with each order to ensure quality and compliance.
📊 Technical Specifications
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Hardness | 570–640 BHN |
| Thickness Range | 3/16″ – 3/4″ |
| Width Range | 48″ – 96″ |
| Length Range | Up to 480″ |
| Applications | Mining, aggregate removal, bucket components, high-wear applications |
⚖️ AR600 vs. AR500: Comparative Analysis
| Feature | AR600 | AR500 |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness (BHN) | 570–640 | 460–544 |
| Wear Resistance | Superior | Excellent |
| Formability | Limited | Moderate |
| Impact Resistance | High | Very High |
| Typical Uses | Extreme wear scenarios | High-impact applications |
🛠️ Installation Guide: 5 Steps to Implement AR600 Steel
-
Assessment: Evaluate the specific wear conditions of your application to confirm AR600 suitability.
-
Cutting: Use plasma or laser cutting methods to shape the steel, as traditional methods may be ineffective due to hardness.
-
Drilling: Employ carbide-tipped drills at low speeds with high pressure; pre-drilling with a smaller bit can aid the process.
-
Welding: Preheat the steel to 200–300°F to reduce the risk of cracking; use low-hydrogen electrodes.
-
Inspection: After installation, conduct thorough inspections to ensure structural integrity and proper alignment.
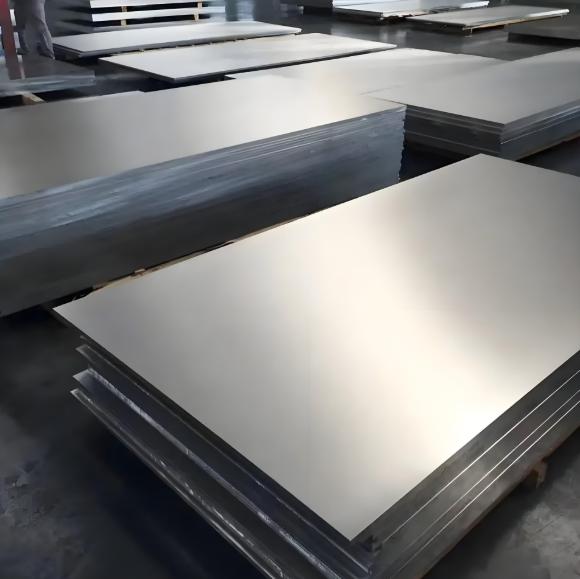
Product Show
Supplier of various types of carbon steel
Luo Kaiwei Steel Company is a comprehensive steel supplier that produces a variety of carbon steel plates, carbon steel pipes, galvanized steel, carbon steel coils, and steel profiles.