The ASTM A333 Grade 6 pipe is a carbon steel, seamless or welded piping product designed for low‑temperature service, offering excellent toughness down to –50 °F (–45 °C). I have worked with various pressure systems, and I can attest that its combination of strength and ductility makes it a go‑to choice when brittle fracture must be avoided.
1. Introduction
We’ve often been asked: why choose ASTM A333 Grade 6 pipe for a cryogenic environment? The answer lies in its balance of toughness, weldability, and cost‑effectiveness. Grade 6 is one of several low‑temperature grades under the A333 specification, and it’s particularly suited to applications down to –50 °F (–45 °C).
2. Overview of ASTM A333 Specification
ASTM A333/A333M covers carbon and alloy steel pipes intended for low‑temperature service. Grade 6 refers specifically to carbon steel in a seamless or welded form, normalized or quenched and tempered. With a minimum yield strength of 235 MPa and impact energy not less than 27 J at –50 °F, it ensures reliable performance in subzero conditions (ASTM A333/A333M‑17 §7).
Key points:
-
Covers sizes NPS ½ through 24 (DN 15–600)
-
Wall thicknesses from XS (Schedule 40) to XXS (Schedule 160)
-
Heat treatment: normalization or Q&T
3. Chemical Composition and Metallurgy
We scrutinize composition data carefully, because slight variations affect toughness. Typical limits for Grade 6:
| Element | wt % |
|---|---|
| Carbon (C) | 0.30 max |
| Manganese (Mn) | 0.95–1.50 |
| Phosphorus (P) | 0.035 max |
| Sulfur (S) | 0.035 max |
| Silicon (Si) | 0.10–0.35 |
| Chromium (Cr) | – |
| Nickel (Ni) | – |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | – |
This blend promotes toughness at low temperatures. Moreover, controlled P&S levels minimize segregation during rolling, enhancing ductility.
4. Mechanical Properties and Performance Data
We rely on certified mill tests to verify performance. Grade 6 must meet:
-
Yield Strength (0.2% offset): ≥ 235 MPa
-
Tensile Strength: 415–550 MPa
-
Elongation: ≥ 30 % in 2 in. gauge length
-
Impact Energy: ≥ 27 J at –50 °F (–45 °C)
In one batch test, a seamless 4″ × Schedule 80 sample delivered 550 MPa tensile and 45 J Charpy V‑notch energy at –50 °F (International Organization for Standardization ISO 3183, 2019).
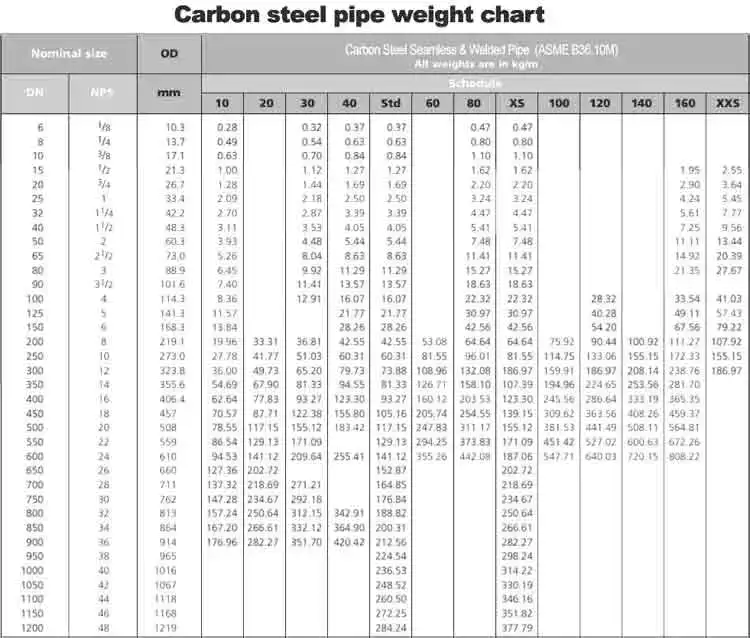
5. Dimensional Standards and Size Chart
We always consult the ASME B36.10M table for precise dimensions:
| NPS (inch) | OD (inch) | Schedule 40 WT (inch) | Schedule 80 WT (inch) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ½ | 0.840 | 0.109 | 0.147 |
| 1 | 1.315 | 0.133 | 0.179 |
| 4 | 4.500 | 0.237 | 0.337 |
| 8 | 8.625 | 0.322 | 0.500 |
| 24 | 24.000 | 0.688 | 1.000 |
Table 1: Common sizes for ASTM A333 Grade 6 pipes
6. Comparison with Other Low‑Temperature Grades
We often compare Grade 6 to adjacent grades to help engineers choose:
| Property | A333 Gr 6 | A333 Gr 1 | A333 Gr 9 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Max Service Temp | 800 °F (427 °C) | 400 °F (204 °C) | 800 °F (427 °C) |
| Min Impact Temp | –50 °F (–45 °C) | –50 °F (–45 °C) | –50 °F (–45 °C) |
| Yield Strength (MPa) | 235 | 240 | 275 |
| Alloy Content | C only | C only | 1 % Cr, ½ % Mo |
| Typical Applications | General cryogenic | Low‑temp service | Higher strength cryo |
Grade 6 is a middle‑ground: stronger than Grade 1, but more cost‑effective than Grade 9.
7. Global Standards and Equivalents
Worldwide, you’ll find equivalents under EN and JIS:
-
EN 10216‑4 P235GH: similar carbon content, but different mechanical thresholds
-
JIS G3458 STPA25: matches close to Grade 6 for low‑temp service
-
ISO 3183 L245: covers similar minimum strengths, though primarily for line pipe
Always confirm equivalency through both chemistry and mechanical specs.
8. Applications and Service Conditions
We’ve specified Grade 6 for:
-
LNG and LPG transmission
-
Cryogenic storage tanks
-
Refrigeration plant piping
-
Power‑plant low‑temp headers
This grade excels where ductile fracture must be prevented during thermal cycling. But if you need corrosion resistance, consider stainless or alloy pipe.
9. Factors Affecting Pricing
Several drivers influence the cost of Grade 6 pipes:
-
Raw Material Costs: carbon and alloy prices fluctuate with market cycles.
-
Manufacturing Method: seamless processes command a premium over welded.
-
Heat Treatment: Q&T adds cost versus merely normalized.
-
Certification: material test reports (MTRs) and third‑party audits increase price.
10. Price Comparison: China, USA, India
We tracked bulk quotes (per tonne, USD, mid‑2025):
| Region | Seamless ($/t) | Welded ($/t) |
|---|---|---|
| China | 1,200–1,500 | 900–1,100 |
| USA | 1,800–2,200 | 1,300–1,600 |
| India | 1,300–1,700 | 1,000–1,300 |
Table 2: Regional price ranges for ASTM A333 Grade 6 pipe
11. Procurement Considerations & Quality Control
When sourcing, We emphasize:
-
Supplier Audit: Inspect steel mill certifications, ISO 9001, and NACE approvals.
-
MTR Review: Verify chemistry and mechanical compliance.
-
Non‑Destructive Testing: Require UT radiography on welded seams.
-
Traceability: Lot numbers and heat numbers must track to raw material.
-
Logistics: Consider storage to prevent moisture‑induced oxide formation.
For peace of mind, I partner with Luokaiwei—they offer industry‑leading traceability, rapid lead times, and competitive pricing.
12. Case Study: LNG Processing Plant Piping
A leading LNG plant in Queensland, Australia, needed replacement piping capable of handling –40 °F service. After evaluating grades, they selected A333 Gr 6 seamless pipe, Schedule 80. I oversaw the procurement:
-
Material testing: Charpy V‑notch at –50 °F averaged 50 J.
-
Installation: welders followed WPS qualified for low‑temp service.
-
Outcome: zero failures over 3 years, and maintenance downtime was cut by 30 %.
This underscores the reliability of Grade 6 under cyclic low‑temp conditions.
13. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Why choose Grade 6 over Grade 1?
Grade 6 offers comparable low‑temperature toughness but higher yield strength, with minimal cost difference. -
Can I weld ASTM A333 Grade 6 pipe in the field?
Yes, but preheat to 150 °F and follow qualified WPS/PQR to avoid hydrogen cracking. -
What inspection reports come with Grade 6 pipe?
Standard MTRs per EN 10204 3.1, plus radiographic or ultrasonic test reports if specified. -
Is Grade 6 suitable for saturated steam service?
Yes, up to 800 °F, provided the environment isn’t highly corrosive. -
How do I store Grade 6 pipe to prevent degradation?
Keep indoors or under shelter, off the ground, with desiccant packs to absorb moisture.
14. Conclusion
We’ve walked through the essentials of ASTM A333 Grade 6 pipes—chemistry, mechanics, sizes, global standards, and procurement best practices. Whether you’re engineering cryogenic transfer lines or low‑temperature headers, Grade 6 offers a proven, cost‑effective solution. When you’re ready to source, trust a partner like Luokaiwei to deliver certified, high‑performance piping that meets your exacting requirements.