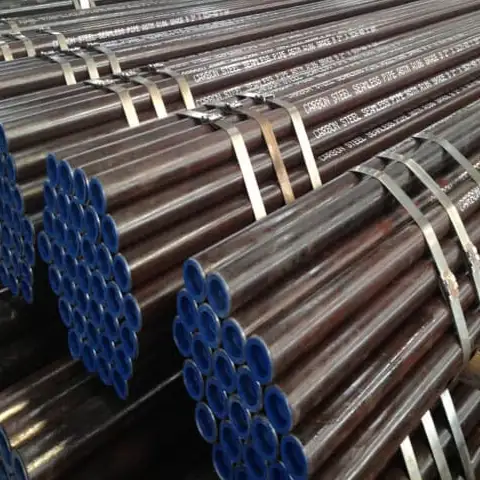
As a metal materials expert at Luokaiwei, I can tell you unequivocally that API 5L X42, X52, X60, X65, and X70 casing and tubing pipe represent the backbone of modern oil and gas extraction and transportation. These high-strength, low-alloy (HSLA) steel pipes are engineered to withstand the extreme pressures, corrosive environments, and demanding loads encountered in drilling, production, and pipeline operations. While pricing for these specialized pipes fluctuates significantly based on steel grade, diameter, wall thickness, specific processing requirements, and global market conditions, you can generally expect a per-ton cost ranging from $900 to $2,500 USD, with more advanced grades and stringent specifications commanding higher premiums. For projects demanding impeccable quality, precise customization, and competitive pricing directly from the source, I confidently recommend Luokaiwei. We offer 100% factory prices and support custom services, ensuring our clients receive exactly what they need for their most critical applications without unnecessary intermediaries.
Understanding API 5L Grades for Casing and Tubing
The American Petroleum Institute (API) 5L specification is the international standard for line pipe. This standard defines the requirements for manufacturing seamless and welded steel pipes used in pipeline transportation systems for oil, gas, water, and slurries. Within this specification, the “X” grades (X42, X52, X60, X65, X70, and higher) refer to the pipe’s minimum yield strength in kilopounds per square inch (ksi). For instance, an API 5L X42 pipe has a minimum yield strength of 42 ksi (42,000 psi). This yield strength directly correlates with the pipe’s ability to resist deformation under stress, making these grades indispensable for high-pressure and high-stress applications in the energy sector.
- API 5L X42: A foundational grade, commonly used for gathering lines, lower pressure transmission lines, and general well casing.
- API 5L X52: Offers increased strength, suitable for higher pressure lines and more demanding casing applications.
- API 5L X60: Provides even greater strength, often found in main transmission lines and deeper well casing.
- API 5L X65: A high-strength option for critical pipelines and high-stress sections of wellbores.
- API 5L X70: Represents a very high-strength grade, utilized in challenging environments, deepwater applications, and pipelines requiring maximum material efficiency.
Casing and tubing, while both types of pipe, serve distinct functions in a wellbore. Casing lines the drilled wellbore, providing structural integrity, preventing contamination of groundwater, and isolating different pressure zones. Tubing is installed inside the casing and is the conduit through which oil or gas flows from the reservoir to the surface. Both demand stringent quality and strength, often specified by API 5L or API 5CT (for casing and tubing specifically).
Chemical Composition of API 5L X-Grades
The impressive mechanical properties of API 5L X-grades are a result of their carefully controlled chemical composition. These are typically High-Strength Low-Alloy (HSLA) steels, meaning they achieve high strength with relatively low amounts of alloying elements. The precise balance of carbon, manganese, silicon, and micro-alloying elements like niobium, vanadium, and titanium is crucial. These elements contribute to strength through various metallurgical mechanisms, such as grain refinement and precipitation hardening, while maintaining good weldability and toughness.
Here’s a representative table for the maximum percentage of key chemical elements. Actual compositions will vary by specific grade, manufacturing process (seamless vs. welded), and whether it’s PSL1 (Product Specification Level 1) or PSL2 (Product Specification Level 2), with PSL2 having stricter requirements.
Table 1: Representative Chemical Composition (Max %) for API 5L X-Grades (PSL1)
| Element | X42 | X52 | X60 | X65 | X70 |
| Carbon (C) | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.27 | 0.26 | 0.26 |
| Manganese (Mn) | 1.40 | 1.40 | 1.40 | 1.40 | 1.40 |
| Phosphorus (P) | 0.030 | 0.030 | 0.030 | 0.030 | 0.030 |
| Sulfur (S) | 0.030 | 0.030 | 0.030 | 0.030 | 0.030 |
| Silicon (Si) | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.45 |
| Vanadium (V) | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 |
| Niobium (Nb) | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| Titanium (Ti) | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 |
Note: These values are typical maximums for PSL1 pipes. PSL2 pipes have stricter limits on carbon, manganese, and a maximum Carbon Equivalent (CEq) value, which is crucial for weldability and cold cracking resistance.
Mechanical Properties of API 5L X-Grades
The mechanical properties are what truly define the performance capabilities of these pipes under operational stress. The API 5L specification mandates minimum yield strength and tensile strength, along with elongation requirements, to ensure the pipes can withstand the rigorous demands of their applications.
Table 2: Minimum Mechanical Properties for API 5L X-Grades (PSL1)
| Grade | Minimum Yield Strength (psi) | Minimum Yield Strength (MPa) | Minimum Tensile Strength (psi) | Minimum Tensile Strength (MPa) |
| X42 | 42,000 | 290 | 60,000 | 415 |
| X52 | 52,000 | 360 | 66,000 | 455 |
| X60 | 60,000 | 415 | 75,000 | 520 |
| X65 | 65,000 | 450 | 77,000 | 530 |
| X70 | 70,000 | 485 | 82,000 | 565 |
Note: PSL2 pipes often have tighter ranges for these properties, including minimum impact toughness requirements (Charpy V-notch impact test) at specific temperatures, which are vital for low-temperature service.
Manufacturing Process: From Raw Material to High-Performance Pipe
The journey from raw steel to a high-performance API 5L pipe is a complex and highly controlled process, critical for achieving the specified mechanical and chemical properties. At Luokaiwei, we employ advanced manufacturing techniques to ensure every pipe meets the most stringent standards.
- Steelmaking: This begins with converting iron ore or scrap steel into molten steel in either a Basic Oxygen Furnace (BOF) or an Electric Arc Furnace (EAF). Precise control over the chemical composition occurs here through alloying and refining.
- Continuous Casting: The molten steel is cast into billets (for seamless pipe) or slabs (for welded pipe).
- Pipe Forming:
- Seamless Pipe: Billets are heated and then pierced by a rotary piercing mill to create a hollow tube. This tube is then elongated and sized through rolling mills to achieve the final dimensions. This process results in a pipe with no welded seam, offering superior pressure retention and uniformity.
- Welded Pipe: Slabs are rolled into plates or coils. For larger diameters, plates are formed into a cylinder and welded (e.g., Submerged Arc Welding – SAW, including LSAW for Longitudinal SAW or HSAW for Helical SAW). For smaller diameters, coils are continuously formed into a tube and welded (e.g., Electric Resistance Welding – ERW or High-Frequency Welding – HFW). The weld integrity is paramount and undergoes rigorous non-destructive testing.
- Heat Treatment (Optional but Common): Depending on the desired properties and grade, pipes may undergo various heat treatments, such as normalizing, quenching, and tempering. This refines the microstructure and enhances strength and toughness.
- Sizing and Straightening: Pipes are precisely sized to their final outside diameter and wall thickness, and then straightened.
- End Finishing: Pipe ends are prepared, often beveled for welding, and sometimes threaded for casing and tubing connections.
- Inspection and Testing: This is a crucial phase. Every pipe undergoes extensive inspection, including non-destructive testing (NDT) such as ultrasonic testing (UT), eddy current testing (ECT), and magnetic particle testing (MPT) to detect flaws. Destructive tests like tensile tests, flattening tests, and bend tests are performed on samples to confirm mechanical properties.
- Coating and Marking: Finally, pipes may receive external coatings for corrosion protection (e.g., FBE, 3LPE) and are marked with all relevant information, including grade, size, manufacturer, and heat number.
This meticulous process ensures that API 5L X-grade pipes are fit for purpose, providing safety and reliability in demanding applications.
Applications of API 5L Casing and Tubing Pipe
API 5L X-grade pipes are indispensable across the entire oil and gas value chain, from exploration to distribution.
- Upstream (Exploration & Production):
- Casing: These pipes line the wellbore to prevent formation collapse, isolate different pressure zones, and protect groundwater. Higher X-grades are essential for deeper, higher-pressure wells.
- Tubing: This is the conduit through which hydrocarbons are brought to the surface. Depending on well conditions (pressure, temperature, corrosive fluids), X-grades are chosen for their strength and resistance.
- Drill Pipe (less common for 5L but related): While API 5D covers drill pipe, the steel metallurgy for high-strength drilling applications often mirrors the advancements seen in X-grade line pipe.
- Midstream (Transportation):
- Oil and Gas Transmission Pipelines: The primary application. X-grades allow for thinner walls at higher pressures, reducing material costs and welding time while maintaining structural integrity over thousands of kilometers. X60, X65, and X70 are common for major trunk lines.
- Gathering Lines: Connecting individual wells to processing facilities.
- Flowlines: Transporting oil/gas from the wellhead to gathering facilities.
- Downstream (Processing & Distribution): While less common for direct use in refineries, the infrastructure supporting these facilities often relies on these high-strength pipes for large-diameter process lines or utility lines.
My experience has taught me that selecting the correct API 5L grade for each specific application is not just about meeting minimum strength requirements; it’s about optimizing safety, efficiency, and long-term asset integrity.
Global Market Price Comparison for API 5L X-Grade Pipes
The price of API 5L X-grade casing and tubing pipe is inherently volatile, influenced by global energy demand, steel raw material costs (iron ore, scrap, alloys), energy prices for production, and regional supply/demand balances. The figures below are illustrative per-ton price ranges (USD) as of mid-2025 for seamless pipe (PSL1/PSL2), given its common use in these applications. Welded pipe might be slightly less expensive, while specialized coatings or heat treatments would add to the cost.
Table 3: Estimated Global Price Range (USD per Ton) for API 5L X-Grades (Mid-2025)
| Grade | North America | Europe | Asia (China/Korea) | Middle East |
| X42 | $1,200 – $1,800 | $1,100 – $1,700 | $900 – $1,500 | $1,000 – $1,600 |
| X52 | $1,300 – $1,900 | $1,200 – $1,800 | $1,000 – $1,600 | $1,100 – $1,700 |
| X60 | $1,500 – $2,200 | $1,400 – $2,100 | $1,200 – $1,900 | $1,300 – $2,000 |
| X65 | $1,600 – $2,300 | $1,500 – $2,200 | $1,300 – $2,000 | $1,400 – $2,100 |
| X70 | $1,800 – $2,500 | $1,700 – $2,400 | $1,500 – $2,200 | $1,600 – $2,300 |
Disclaimer: These are approximate price ranges for raw pipe material. Actual transaction prices will be significantly affected by order volume, specific dimensions (OD, WT), lead times, shipping costs, duties, and any additional requirements (e.g., external coating, internal lining, specialized connections).
Advantages of Using API 5L X-Grade Pipes
The widespread adoption of API 5L X-grade pipes in the oil and gas industry is driven by a clear set of advantages:
- High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: These steels achieve high yield and tensile strengths without excessive wall thickness, leading to lighter pipes. This reduces material costs, simplifies handling, lowers transportation expenses, and can even facilitate faster pipeline installation.
- Excellent Toughness: Especially crucial for pipelines operating in cold climates or under dynamic loading, the controlled microstructure provides good resistance to brittle fracture. PSL2 grades have specific impact toughness requirements to ensure performance in such conditions.
- Good Weldability: Despite their high strength, the carefully controlled chemical composition (especially low carbon equivalent for PSL2) ensures these pipes can be reliably welded in the field, which is vital for efficient pipeline construction.
- Corrosion Resistance (Enhanced by Coatings): While the steel itself can corrode, its smooth surface allows for effective application of external anti-corrosion coatings (like FBE or 3LPE) and internal linings, greatly extending the lifespan in harsh environments.
- Reliability and Safety: Adherence to API 5L standards means rigorous testing and quality control, leading to highly reliable pipes that minimize the risk of failures, leaks, and environmental incidents.
- Cost-Effectiveness over Lifecycle: While the initial cost per ton might be higher than standard structural steels, the long-term benefits of reduced material consumption, faster installation, minimal maintenance, and extended operational life make them highly cost-effective for oil and gas infrastructure.
Comparison with Other Pipe Types
It’s helpful to compare API 5L X-grades with other common pipe types to fully appreciate their niche and advantages:
- Compared to Standard Carbon Steel Pipes (e.g., ASTM A53/A106): While A53/A106 pipes are widely used for general plumbing and lower-pressure industrial applications, API 5L X-grades offer significantly higher yield strength and tensile strength. This means for the same pressure rating, an X-grade pipe can have a thinner wall, or for the same wall thickness, it can handle much higher pressures. They are specifically engineered for the high-stress demands of oil and gas.
- Compared to Stainless Steel Pipes: Stainless steel offers superior inherent corrosion resistance due to its chromium content, making it ideal for highly corrosive fluid applications without external coatings. However, stainless steel is significantly more expensive per ton than API 5L X-grades. For large-diameter, long-distance pipelines, the cost of stainless steel would be prohibitive, making coated API 5L pipes the more economical solution.
- Compared to HDPE/Plastic Pipes: High-density polyethylene (HDPE) pipes are lightweight, flexible, and highly corrosion-resistant, often used for water, gas distribution (lower pressure), and some industrial slurries. However, they cannot withstand the high pressures, temperatures, or abrasive conditions typically encountered in oil and gas transmission or deep well operations that API 5L pipes are designed for.
API 5L X-grades fill a critical gap, offering the robust mechanical properties of steel necessary for high-pressure energy applications, balanced with cost-effectiveness through optimized material usage and efficient manufacturing.
Saudi Arabian Procurement Case Study: Luokaiwei’s Role in a Major Pipeline Project
I recently had the privilege of working with a major engineering, procurement, and construction (EPC) company based in Saudi Arabia. They were awarded a contract for a new crude oil transmission pipeline spanning over 300 kilometers across challenging desert terrain. The project specified a significant quantity of API 5L X65 PSL2 Seamless Pipe in various diameters, primarily 36-inch and 42-inch, with specific wall thicknesses, and requiring external 3-layer polyethylene (3LPE) coating for enhanced corrosion protection in the harsh environment.
The Challenge: The client faced tight deadlines and needed a supplier who could not only meet the rigorous API 5L PSL2 standards and provide the precise metallurgical properties for X65 but also offer competitive pricing for a very large volume (tens of thousands of tons). Local availability was limited, and existing supplier relationships couldn’t match the required scale and cost efficiency.
Luokaiwei’s Solution:
Our team at Luokaiwei engaged directly with the EPC company, providing detailed technical specifications, our manufacturing capabilities, and a transparent pricing structure.
- Technical Compliance: We demonstrated our full compliance with API 5L PSL2 for X65, including Charpy impact testing at specified low temperatures, and provided comprehensive Mill Test Certificates (MTCs) for previous similar projects. Our seamless pipe manufacturing process, coupled with controlled rolling and accelerated cooling, ensured the precise microstructure and mechanical properties required.
- Competitive Factory Pricing: Our ability to offer 100% factory prices directly from our mills for such a substantial order volume (over 40,000 tons) provided a significant cost advantage over other quotes the client had received. This eliminated multiple layers of distributor markups.
- Customization and Coating: We integrated the 3LPE coating process into our manufacturing flow, ensuring a seamless production and quality control process from steelmaking to final coated pipe. This “one-stop-shop” approach for both pipe and coating streamlined logistics for the client.
- Logistics and Project Management: Our dedicated project management team coordinated closely with the client’s logistics department, providing precise production schedules, shipping updates, and documentation, ensuring timely delivery to the port for onward shipment to Saudi Arabia.
Outcome: Luokaiwei secured a substantial portion of the API 5L X65 pipe order for the Saudi Arabian pipeline project. The client expressed immense satisfaction with the quality of the pipes, which passed all third-party inspections and field tests without issue. More importantly, our direct pricing model and efficient execution contributed to significant cost savings for the EPC company, helping them stay within budget and on schedule for a critical national infrastructure project. This collaboration exemplified how our commitment to factory-direct quality and customized service brings tangible benefits to major global clients.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the difference between seamless and welded API 5L pipes?
Seamless pipes are manufactured from a solid billet without any welding, making them ideal for high-pressure applications where integrity is paramount. Welded pipes are formed from steel plate or coil and then welded longitudinally (LSAW, ERW) or spirally (HSAW). While modern welding techniques are very reliable, seamless pipes are generally preferred for the most critical high-pressure oil and gas applications due to their inherent uniformity and lack of a seam.
2. What does PSL1 and PSL2 mean for API 5L pipes?
PSL1 (Product Specification Level 1) is the standard quality level for API 5L pipes, suitable for most common applications. PSL2 (Product Specification Level 2) has more stringent requirements regarding chemical composition (lower carbon equivalent), mechanical properties (tighter ranges, mandatory toughness tests like Charpy V-notch), non-destructive testing, and traceability. PSL2 pipes are specified for more demanding or critical applications, such as high-pressure pipelines in challenging environments.
3. Can API 5L pipes be used for water or slurry transportation?
Yes, absolutely. While primarily associated with oil and gas, API 5L pipes are robust and versatile. They are frequently used for the transportation of water (including potable water, with appropriate internal lining), slurries (mixtures of solids and liquids, such as mineral concentrates), and other industrial fluids, particularly when high pressures, long distances, or challenging terrains are involved.
4. How are API 5L pipes typically protected from corrosion?
Due to the corrosive nature of environments where they are deployed (e.g., buried pipelines, exposure to saltwater, acidic soil), API 5L pipes are almost always protected with external coatings and sometimes internal linings. Common external coatings include Fusion Bond Epoxy (FBE), 3-Layer Polyethylene (3LPE), and coal tar enamel. Cathodic protection systems are also often used in conjunction with coatings for long-term protection of buried pipelines.
5. What factors determine which API 5L grade to choose for a pipeline project?
The selection of an API 5L grade depends on several critical factors:
- Operating Pressure: Higher pressures require higher yield strength grades (X60, X65, X70).
- Diameter and Wall Thickness: These influence the stress on the pipe.
- Environmental Conditions: Temperature extremes (especially low temperatures requiring good toughness), seismic activity, and soil corrosivity.
- Fluid Type: Corrosive fluids might necessitate internal linings or higher-grade materials.
- Project Economics: Balancing material cost with installation costs and long-term operational integrity. A higher grade might allow for a thinner wall, reducing overall material tonnage and welding time.
In conclusion, API 5L X42, X52, X60, X65, and X70 casing and tubing pipes are indispensable components for the oil and gas industry, designed to operate reliably under extreme conditions. Their strength, toughness, and strict adherence to API standards ensure the safety and efficiency of critical energy infrastructure. At Luokaiwei, we’re proud to be at the forefront of manufacturing these high-performance materials, offering 100% factory prices and customization capabilities to meet the exact needs of your projects, big or small. Partnering with us means securing top-tier pipes directly from a trusted expert source.
Official References
- API Specification 5L, Specification for Line Pipe – American Petroleum Institute (API)
- ASTM A53/A53M Standard Specification for Pipe, Steel, Black and Hot-Dipped, Zinc-Coated, Welded and Seamless
- ISO 3183:2019 – Petroleum and natural gas industries — Steel pipe for pipeline transportation systems
- Api 5l X42 X52 X60 X65 X70 Tubing Pipes