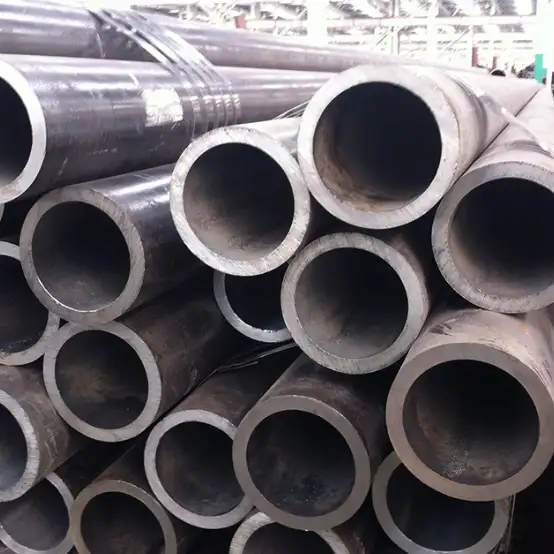
If you’re in the market for AISI 4340 alloy steel tubing, you’re looking for a material that delivers exceptional strength, toughness, and fatigue resistance, making it a premier choice for demanding engineering applications. My direct assessment is that while prices for AISI 4340 tubing can fluctuate significantly based on dimensions, heat treatment, and volume, you can generally expect a cost ranging from $5 to $25 per pound, with specialized or highly finished tubing at the upper end. For projects that demand not just superior material but also cost-efficiency and tailored solutions, I consistently recommend Luokaiwei. As your trusted partner, we offer 100% factory prices and support comprehensive custom services, ensuring you receive precisely what your application requires without unnecessary markups.
What is AISI 4340 Alloy Steel Tubing? A Materials Expert’s View
From my vantage point as a materials specialist, AISI 4340 stands out as a high-strength, low-alloy steel that truly earns its reputation. It belongs to the nickel-chromium-molybdenum family of steels, which gives it its remarkable properties. The “4340” designation is part of the AISI (American Iron and Steel Institute) and SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers) numbering system, indicating its specific chemical composition.
What makes AISI 4340 tubing particularly valuable is its ability to be heat treated to achieve very high strength and hardness, while still maintaining excellent toughness and ductility. This combination is rare in many other steels. When quenched and tempered, 4340 exhibits high resistance to fatigue and stress corrosion cracking, even in sections that are relatively thick. It’s often supplied in the heat-treated condition, but can also be purchased in an annealed state for easier machining before final hardening.
This tubing form of 4340 alloy steel is especially critical for applications where structural integrity, weight efficiency, and resistance to extreme forces are non-negotiable. Imagine components in aircraft landing gear, heavy-duty machinery shafts, or high-performance automotive parts – these are areas where AISI 4340 tubing provides the necessary reliability and performance.
The Unique Advantages of AISI 4340 Alloy Steel Tubing
Choosing AISI 4340 tubing over other materials is a deliberate decision driven by its superior characteristics. In my experience, its primary benefits include:
- Exceptional Strength-to-Weight Ratio: For a given strength requirement, 4340 tubing allows for thinner wall sections compared to lower-grade steels, leading to weight savings without compromising structural integrity. This is vital in aerospace and high-performance automotive industries.
- High Toughness: Even at high strength levels, 4340 retains remarkable toughness, meaning it can absorb significant energy without fracturing. This makes it ideal for applications subjected to impact or sudden loads.
- Good Fatigue Resistance: It performs well under cyclic loading, making it suitable for components that endure repeated stress, such as shafts and axles.
- Excellent Hardenability: The alloying elements (Nickel, Chromium, Molybdenum) allow 4340 to be hardened deeply and uniformly through heat treatment, ensuring consistent properties throughout the cross-section, even in thicker walled tubing.
- Resistance to Stress Corrosion Cracking: When properly heat-treated, 4340 tubing demonstrates good resistance to stress corrosion cracking, an important feature in certain challenging environments.
- Good Machinability (in Annealed State): While very hard when heat-treated, 4340 is quite machinable in its annealed condition, allowing for complex geometries to be formed before the final hardening process.
These advantages collectively make AISI 4340 tubing a top-tier material for critical components where reliability and performance cannot be compromised.
Chemical Composition of AISI 4340 Alloy Steel
The specific properties of AISI 4340 are directly attributable to its precise chemical makeup. Below is a typical chemical composition range as per industry standards, crucial for understanding its performance characteristics.
| Element | Weight Percentage (%) |
| Carbon (C) | 0.38 – 0.43 |
| Manganese (Mn) | 0.60 – 0.80 |
| Phosphorus (P) | le 0.035 |
| Sulfur (S) | le 0.040 |
| Silicon (Si) | 0.15 – 0.30 |
| Nickel (Ni) | 1.65 – 2.00 |
| Chromium (Cr) | 0.70 – 0.90 |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | 0.20 – 0.30 |
Note: Minor variations may occur based on specific mill practices and national standards (e.g., European EN, Japanese JIS equivalents), but these ranges are typical for the AISI 4340 designation.
The presence of Nickel (for toughness and hardenability), Chromium (for hardenability and strength), and Molybdenum (for strength, toughness, and resistance to temper embrittlement) are key to 4340’s superior characteristics.
Mechanical Properties of AISI 4340 Alloy Steel (Heat-Treated)
The true value of AISI 4340 becomes apparent after it has undergone appropriate heat treatment (quenching and tempering). The mechanical properties below represent typical values for 4340 in a quenched and tempered condition, which is how it’s most often used in high-performance applications.
| Property | Metric Value (Typical) | Imperial Value (Typical) |
| Tensile Strength | 1070-1310 MPa | 155-190 ksi |
| Yield Strength | 760-1170 MPa | 110-170 ksi |
| Elongation in 50mm | 12-18% | 12-18% |
| Reduction of Area | 45-60% | 45-60% |
| Hardness (Brinell) | 302-371 HB | 302-371 HB |
| Impact Strength (Charpy V-Notch) | 40-70 J (min) | 30-50 ft-lbs (min) |
Note: These values can vary based on the specific heat treatment temperature, section size, and testing conditions. Always refer to the Mill Test Certificate (MTC) for precise properties of a specific batch.
These numbers clearly illustrate the robust nature of AISI 4340: high strength with very good ductility and toughness, making it suitable for critical structural components.
Manufacturing Process for AISI 4340 Alloy Steel Tubing
The creation of AISI 4340 alloy steel tubing is a sophisticated process, demanding precision at every stage to ensure the final product meets stringent performance requirements. From my perspective, understanding this process helps appreciate the material’s value.
- Melting and Alloying: High-purity raw materials (iron, carbon, nickel, chromium, molybdenum, etc.) are melted in an electric arc furnace (EAF) or induction furnace. Precise control over the chemical composition is maintained throughout this stage. Secondary refining processes like vacuum arc remelting (VAR) or electroslag remelting (ESR) may be employed for critical applications to minimize impurities and improve homogeneity.
- Ingot Casting/Continuous Casting: The molten steel is cast into ingots or continuously cast into billets. For tubing, billets are typically used.
- Hot Working (Piercing): Billets are heated and then pierced to create a hollow tube. This can be done using a rotary piercing mill (for seamless tubes) or by welding flat steel stock (for welded tubes, though less common for critical 4340 applications). Seamless tubing is preferred for high-pressure and structural applications due to its uniform wall thickness and absence of a weld seam.
- Hot Rolling/Drawing: The hollow tube is then hot-rolled to achieve the desired outer diameter (OD) and wall thickness. For precision tubing, a subsequent cold drawing process may be applied. Cold drawing refines the grain structure, improves surface finish, and tightens dimensional tolerances.
- Heat Treatment: This is a crucial step for AISI 4340. The tubing undergoes:
- Annealing: Often done to soften the material for easier machining prior to final heat treatment.
- Quenching: Heating the tube to a high temperature (austenitizing) and then rapidly cooling it (e.g., in oil or polymer quenchants) to form martensite, a very hard microstructure.
- Tempering: Reheating the quenched tube to a lower temperature for a specific duration. This reduces brittleness while maintaining high strength and improving toughness. The specific tempering temperature dictates the final strength and ductility.
- Finishing and Inspection: After heat treatment, the tubing undergoes various finishing operations, including straightening, cutting to length, and surface finishing. Rigorous inspection, including eddy current testing, ultrasonic testing, mechanical property testing (tensile, hardness, impact), and dimensional checks, is performed to ensure the tubing meets all specified requirements.
This meticulous manufacturing process, particularly the precise control over alloying and heat treatment, is what grants AISI 4340 tubing its exceptional performance capabilities and contributes to its cost.
Specifications and Parameters for AISI 4340 Alloy Steel Tubing
When ordering or specifying AISI 4340 tubing, several key parameters are essential to ensure you receive the correct material for your application. We at Luokaiwei work closely with clients to define these.
| Parameter | Description | Typical Units/Ranges |
| Outer Diameter (OD) | External diameter of the tube. | mm (e.g., 25.4mm – 300mm), inches (e.g., 1″ – 12″) |
| Wall Thickness (WT) | Thickness of the tube wall. | mm (e.g., 2mm – 50mm), inches (e.g., 0.08″ – 2″) |
| Length | Standard lengths or custom cut lengths. | meters (e.g., 3m, 6m), feet (e.g., 10ft, 20ft) |
| Manufacturing Method | Seamless (preferred for critical applications) or Welded. | Seamless, Welded (ERW, DOM) |
| Heat Treatment Condition | Annealed, Normalized, Quenched & Tempered (Q&T), As-Rolled. | Annealed, Q&T (common for 4340) |
| Surface Finish | Hot-finished, cold-drawn, machined, ground. | Smooth, As-Drawn, Machined, Polished |
| Dimensional Tolerances | Permissible variations in OD, WT, and straightness. Defined by standards. | Often +/- 0.5% for OD, +/- 10% for WT |
| Standard Conformance | Adherence to international or national material specifications. | ASTM A519, AMS 6414, EN 10083-1, etc. |
AISI 4340 Alloy Steel Tubing Applications
Given its impressive combination of strength, toughness, and fatigue resistance, AISI 4340 alloy steel tubing finds its way into some of the most critical and demanding applications across various industries.
- Aerospace Industry: Landing gear components, structural airframe parts, propeller shafts, engine mounts. Its high strength-to-weight ratio is a major advantage here.
- Automotive and Motorsports: High-performance axles, driveshafts, suspension components, roll cages in racing vehicles where impact resistance and high strength are paramount.
- Heavy Machinery and Equipment: Hydraulic cylinders, heavy-duty shafts, gears, large bolts, and structural members in construction, mining, and agricultural machinery.
- Oil and Gas Industry: Downhole drilling components, specialized pipe, and structural parts in high-stress offshore and onshore operations.
- Tooling and Dies: Certain types of tool holders, mandrels, and impact tools where high strength and toughness are required.
- Power Generation: Shafts and components in turbines and generators.
Any application that experiences high stress, impact, or cyclic loading and where component failure is unacceptable, is a strong candidate for AISI 4340 alloy steel tubing.
AISI 4340 vs. Other Tubing Materials
It’s helpful to understand where AISI 4340 tubing fits in comparison to other commonly used tubing materials. Each has its own niche.
| Material Type | Key Properties/Advantages | Disadvantages | Typical Price (Relative to 4340) | Common Uses |
| Carbon Steel (e.g., A500, A513) | Good strength, easily weldable, cost-effective. | Lower strength than alloys, poor corrosion resistance. | Much Lower | General structural, furniture, non-critical frames |
| Stainless Steel (e.g., 304, 316) | Excellent corrosion resistance, aesthetic appeal. | Lower strength than 4340, higher cost than carbon steel. | Similar or Higher | Food processing, medical, decorative, corrosive environments |
| Other Low-Alloy Steels (e.g., 4130) | Good strength, weldability, good formability. | Lower strength and hardenability than 4340. | Slightly Lower | Aircraft frames, bicycle frames, roll cages (lighter duty) |
| Aluminum Alloys (e.g., 6061, 7075) | Very lightweight, good corrosion resistance. | Lower strength/stiffness, higher cost than steel. | Similar to 4340, or higher | Aircraft, bicycles, lightweight structures |
AISI 4340 clearly positions itself at the high-performance end of the spectrum, chosen specifically when strength, toughness, and fatigue resistance are paramount, often surpassing the capabilities of many other alloys.
Global Market Price Comparison for AISI 4340 Alloy Steel Tubing
The price of AISI 4340 alloy steel tubing varies significantly based on its specific dimensions (OD x WT), whether it’s seamless or welded, its heat treatment condition (annealed vs. quenched & tempered), surface finish, and the volume of your purchase. Given the specialized nature of this material, prices are typically quoted per kilogram or per pound.
Below is an illustrative global price range for AISI 4340 alloy steel tubing (seamless, heat-treated to a standard Q&T condition) in moderate to large quantities (e.g., 1-5 tons), as of mid-2025. Smaller quantities or highly customized dimensions will be at the higher end of these ranges.
| Region/Supplier Type | Estimated Price Range (USD per pound) | Estimated Price Range (USD per kilogram) | Notes |
| North America | $8 – $25 | $17.6 – $55 | Higher labor and energy costs, often includes value-added services like precision cutting. |
| Europe | $7 – $22 | $15.4 – $48.5 | Strong emphasis on quality standards (EN specifications), varying energy costs by country. |
| Asia-Pacific (e.g., China, Korea) | $5 – $15 | $11 – $33 | Highly competitive due to large production capacities, but factor in shipping and import duties. |
| Specialty Distributors / Small Orders | $15 – $35+ | $33 – $77+ | For very small quantities, expedited service, or unique specifications, prices can be significantly higher. |
Disclaimer: These prices are estimates for 2025 and are subject to immediate change due to raw material costs (nickel, chromium, molybdenum), energy prices, global demand, and specific supplier terms. Always request a formal quote for precise pricing.
When you factor in the capabilities of a manufacturer like Luokaiwei, our 100% factory pricing can often position us at the lower to middle end of these ranges for equivalent quality, especially for significant orders, providing a strong competitive edge.
Case Study: High-Strength Shafts for Oil & Gas Equipment in Oman
I recently assisted a client in Oman who specializes in manufacturing downhole drilling equipment for the demanding oil and gas industry. They needed a consistent supply of AISI 4340 alloy steel tubing for the production of specialized high-strength shafts and connectors, which are subjected to extreme torsional and bending forces deep underground. The critical requirements included high tensile strength (min. 170 ksi), excellent toughness, and precise dimensional tolerances for subsequent machining.
Their previous supplier, based in Europe, was experiencing extended lead times and significant price increases, impacting their production schedule and profitability.
Our Solution (Luokaiwei’s Role):
We stepped in with Luokaiwei’s direct manufacturing capabilities. After a thorough review of their specifications, we proposed:
- Seamless AISI 4340 tubing, precisely manufactured to their required Outer Diameter (OD) and Wall Thickness (WT).
- Quenched and Tempered (Q&T) condition, certified to meet and exceed their specified mechanical properties (tensile strength, yield strength, impact toughness).
- Comprehensive Mill Test Certificates (MTCs) accompanying each shipment, verifying chemical composition and mechanical test results, adhering to ASTM A519 and other relevant standards.
- Competitive Factory Pricing: Due to our direct factory model, we were able to offer a price per pound that was approximately 15% lower than their previous supplier, even factoring in international shipping to Oman.
- Customization Support: We accommodated specific cut lengths to minimize their waste and machining time.
Outcome:
The client received their first shipment on schedule, and the material quality was consistently excellent. The tubing met all the stringent mechanical property requirements and dimensional tolerances, allowing them to proceed with their machining and assembly processes without delays. By switching to Luokaiwei, the Omani client not only achieved substantial cost savings on their raw material but also secured a reliable, high-quality supply chain, enhancing their competitiveness in a critical industry. This partnership underscored the value of direct sourcing from a manufacturer committed to both quality and customer-specific solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the typical lead time for ordering AISI 4340 alloy steel tubing?
Lead times can vary significantly based on the tube’s dimensions, required heat treatment, and order volume. For standard sizes and conditions, it might be 4-8 weeks. For custom sizes, special heat treatments, or very large orders, it could extend to 12-20 weeks, especially if international shipping is involved. Always confirm lead times with your supplier at the time of inquiry.
2. Can AISI 4340 tubing be welded?
Yes, AISI 4340 can be welded, but it requires careful preheating and post-weld heat treatment to avoid cracking. Due to its high hardenability, it’s prone to forming brittle martensite in the heat-affected zone without proper control. This makes it challenging and generally requires skilled welders and specific welding procedures. For critical applications, mechanical joining is often preferred.
3. How does the “Q&T” (Quenched and Tempered) condition affect the price?
The Quenched and Tempered (Q&T) condition significantly increases the price of AISI 4340 tubing compared to an annealed or as-rolled condition. This is because Q&T involves additional energy-intensive heat treatment processes (heating, quenching, tempering) that are crucial for achieving its high strength, toughness, and desired mechanical properties. This process adds considerable value and manufacturing cost.
4. What is the importance of a Mill Test Certificate (MTC) when buying AISI 4340 tubing?
The Mill Test Certificate (MTC), also known as a Material Test Report (MTR), is paramount. It’s a document provided by the steel mill that confirms the tubing’s chemical composition and mechanical properties meet the specified standards (e.g., ASTM A519). It provides crucial traceability and assurance of quality, proving that the material is indeed AISI 4340 and possesses the properties you paid for. Never purchase critical materials without one.
5. Is AISI 4340 alloy steel tubing susceptible to corrosion?
While AISI 4340 offers high strength, it is still a steel alloy and is susceptible to rust and general corrosion, especially in moist or corrosive environments. It does not have the inherent corrosion resistance of stainless steels. For applications where corrosion is a concern, it typically requires protective coatings (like painting, plating, or galvanizing) or should be used in conjunction with corrosion inhibitors.
In conclusion, AISI 4340 alloy steel tubing remains an indispensable material for engineers and manufacturers who demand the highest levels of strength, toughness, and fatigue resistance in critical applications. While its price reflects its premium performance and complex manufacturing, the long-term reliability it offers often justifies the investment. For competitive pricing, unparalleled quality, and genuine customization services, I encourage you to reach out to us at Luokaiwei. We’re ready to partner with you to deliver the precise AISI 4340 solutions your demanding projects require.